Introduction
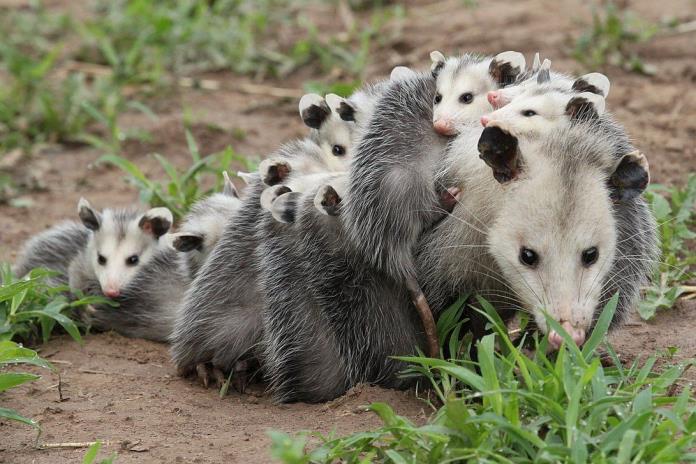
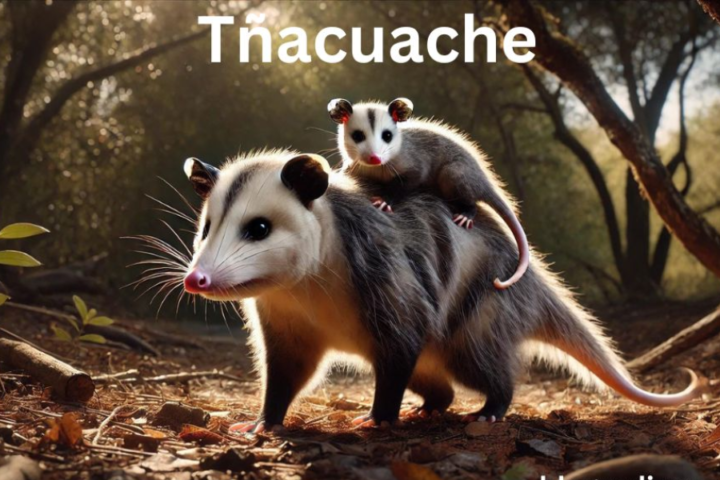
In Mexico, the humble tñacuache , also known as the Mexican opossum, has become a notable fixture not only in rural landscapes but increasingly within bustling urban areas. While often dismissed as a nuisance due to its habit of scavenging through garbage, the tñacuache holds an invaluable role in maintaining the health and balance of urban ecosystems. Conservationists urge us to see beyond its reputation as a pest and recognize its contributions to biodiversity. This article takes a closer look at the tñacuache’s place in Mexico’s ecological landscape, the challenges it faces, and the importance of its conservation.
Habitat
The tñacuache is native to various regions across Mexico and thrives in a wide range of habitats, from dense forests to suburban backyards and city alleys. In rural settings, they are often found close to rivers and moist areas, which provide ample food sources and cover. However, as cities expand and natural habitats shrink, these adaptable animals have become urban dwellers, thriving among humans and adapting to environments filled with opportunities to scavenge.
Diet
The tñacuache is an omnivore with a varied diet that includes insects, fruits, small animals, and even carrion. In urban areas, they have become known for scavenging through garbage bins, which sometimes leads to conflicts with city residents. However, their diet plays a crucial role in controlling insect populations, reducing disease spread, and even limiting the populations of other small animals. These qualities make them beneficial for human environments, especially considering the minimal impact they have compared to other urban wildlife.
Role
Despite their unassuming appearance and misunderstood habits, tñacuaches play a key role in maintaining biodiversity. They are natural scavengers and contribute to waste management by feeding on organic refuse. This not only reduces waste but also helps curb the spread of diseases that might otherwise thrive in decaying materials. By keeping insect populations in check, they contribute to the balance of species in their environments. The tñacuache is, therefore, a vital yet often overlooked contributor to urban ecosystem health.
Threats
The growing presence of tñacuaches in cities also exposes them to unique threats. Urban environments present challenges such as vehicular traffic, reduced green spaces, pollution, and human hostility. In rural areas, their habitats are constantly under threat from agriculture and deforestation. The perception of tñacuaches as pests further complicates their safety, as some residents view them as nuisances rather than beneficial animals.
Conservation
The conservation of the tñacuache requires both public awareness and practical measures. Environmental organizations in Mexico have begun campaigns to educate residents about the importance of protecting tñacuaches, underscoring their ecological role. Conservationists suggest that instead of fearing or despising these animals, people should learn to coexist with them. Strategies such as secure garbage disposal methods and designated green spaces could help reduce conflicts.
Benefits
Supporting the tñacuache population in urban areas offers tangible benefits. For instance, their diet helps control unwanted pests naturally, which reduces the need for chemical pest control. This indirectly supports a healthier environment for humans, as fewer pesticides are used. Additionally, their scavenging can contribute to cleaner public spaces, provided waste is managed appropriately.
Future
The future of the tñacuache in urban ecosystems will depend on conservation efforts and public attitudes. By fostering greater awareness of their role, Mexico can take steps to protect and preserve these animals. With increased green spaces and the adoption of urban planning practices that support wildlife, the tñacuache could continue to thrive while benefiting the human populations around them.
In closing, the tñacuache’s journey from rural forests to city streets serves as a reminder of nature’s adaptability and resilience. Through mindful conservation and a shift in perception, this often-overlooked creature could earn its place as an essential ally in Mexico’s urban landscapes. As we learn to appreciate the tñacuache’s contributions, we open doors to more sustainable urban ecosystems that honor biodiversity and coexistence.